A better way of understanding our yuuvis® Momentum microservices - graphical overviews of the architecture and basic use case flows
Introduction
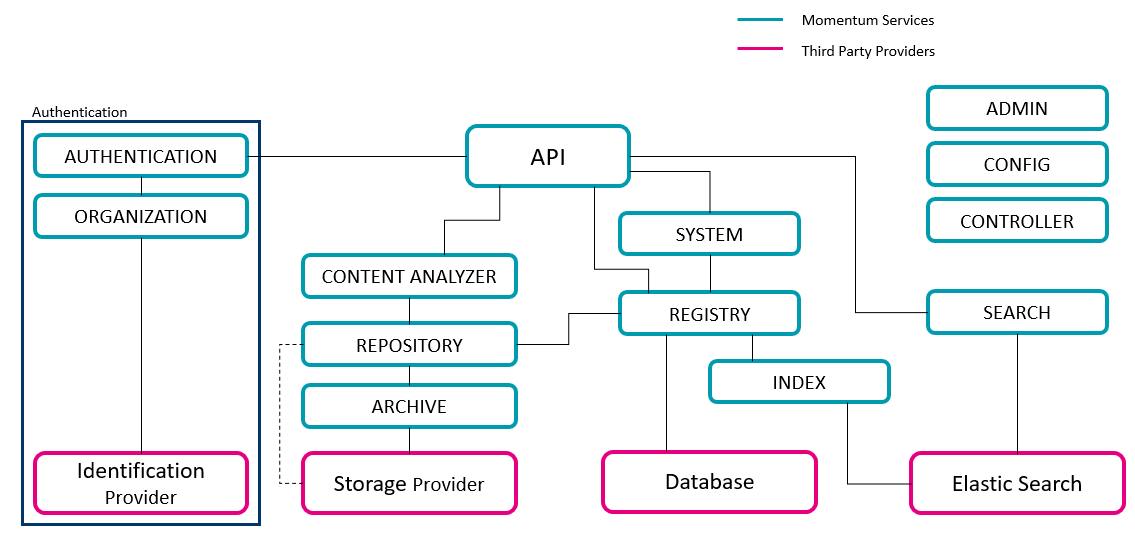
By chunking up the system into microservices it can be tough to keep the overview of all available services, their relationships and dependencies to each other. The following graphical overview of our microservice architecture offers you a first entry point into the yuuvis® Momentum landscape. By providing further and more detailed examples based on special use cases (flows) you'll get a better and easy way of understanding our entire landscape.
Graphical Overview
For visualizing the topology of our microservices the following overview shows - on a higher level - many of our core microservices.
For understanding various flows - on a more granular level - check out the detailed diagrams visualizing special use case.
Login to the Core API - Authentication (Browser / Application)
To interact with yuuvis® it is necessary to log in with a user account. The user accounts are managed by at least one external identity provider.
Click here to show the authentication flow (application) >>
| 1. - HTTP request to any API endpoint, sending basic authentication or bearer token 2. - verify credentials externally 3. - receive auth code to authentication with auth code 4. - request roleset acquisition 5. - query user roleset externally 6. - receive user roleset 7. - present roleset 8. - provide authentication token and proceed with initial API request 9. - request information from other parts of the system 10. - obtain requested information 11. - produce API response 12. - send HTTP response to user
Webhook entry points *1 - user.info |
Click here to show the authentication flow (browser) >>
| 1. - HTTP request to any API endpoint 2. - Redirect to Identification Provider 3. - Verify Credentials externally 4. - Redirect to authentication with Auth code 5. - Send Auth code to Authentication Service 6. - Retrieve UserId using Auth code 7. - Recieve UserId 8. - Request roleset acquisition 9. - Query user roleset 10. - Recieve user roleset 11. - Present roleset 12. - Provide authentication token and Proceed with initial API request 13. - Request information from other parts of the System 14. - Obtain requested information 15. - Produce API response 16. - Send HTTP response to User
Webhook entry points *1 - user.info |
Importing Documents
Documents can be imported into a yuuvis® Momentum system using the provided core API's HTTP requests for importing documents (POST /api/dms/objects).
>> Importing Documents via Core API
Click here to show the import flow >>
| 1. - HTTP Post request containing metadata and content 2. - enrichment of request with authentication token 3. - defer content to storage services 3.1 - analyze content file 3.2 - skip content analyzer 4. - content storage handling 4.1 - using custom storage via archive service 4.2 - using s3 interface of repository 5. - create metadata based on previous steps 6. - write metadata to storage / index instances 7. - index new object in ES 8. - create initial audit entry 9. - create API response from metadata 10. - return metadata as HTTP response During asynchronous import operations, the controller service provides messaging for the boxed in services Webhook entry points *1 - dms.request.import.storage.before *2 - dms.response.objects |
Retrieval of Content by ID / Older Version
The content of already imported documents into the yuuvis® Momentum system can be retrieved using the provided core API's HTTP requests for retrieving content files (GET /api/dms/objects/{objectId}/contents/file). If a specific version of the document's content is to be requested, the endpoint to be called changes and includes the specific version (GET /api/dms/objects/{objectId}/versions/{versionNr}/contents/file).
>> Retrieving Documents via Core API
Click here to show the content retrieval flow by ID >>
| 1. - HTTP get request to object URL 2. - Enrichment of request with authentication Token 3. - Check for User Authorization using search service query 4. - Query elastic search for object ID 5. - Elasticsearch metadata reponse (if user is authorized) 6. - Repository url of objectId 7. - Request content of objectID 8. - Query objectId in Storage Provider 9. - Storage Provider metadata response 10. - Return metadata object metadata 11. - Write CONTENT_ACCESSED audit entry 12. - Create API response from metadata 13. - Return HTTP metadata response Webhook entry points *1 - dms.response.objects |
Click here to show the content retrieval flow by ID (older version) >>
| 1. - HTTP get request to object URL 2. - Enrichment of request with authentication Token 3. - Check for User Authorization using search service query 4. - Query elastic search for object ID 5. - Elasticsearch metadata response (if user is authorized) 6. - Verify that user has object access rights 7. - Retrieve metadata version using Registry Service 8. - Query object metadata version from database 9. - Return metadata including Repository URL of content 10. - Return content Repo URL 11. - Request content of objectID 12. - Query objectId in Storage Provider 13. - Storage Provider metadata response 14. - Return metadata object metadata 15. - Write CONTENT_ACCESSED audit entry 16. - Create API response from metadata 17. - Return HTTP metadata response Webhook entry points *1 - dms.response.objects |
The metadata of already imported documents into the yuuvis® Momentum system can be retrieved using the provided core API's HTTP requests for retrieving the metadata (GET /api/dms/objects/{objectId}). If a specific version or all versions of the document's metadata is to be requested, the endpoints to be called change and include the versions (GET /api/dms/objects/{objectId}/versions / GET /api/dms/objects/{objectId}/versions/{versionNr}).
>> Retrieving Documents via Core API
Click here to show the metadata retrieval flow by ID >>
| 1. - HTTP get request to object URL 2. - Enrichment of request with authentication Token 3. - Request metadata 4. - Query objectId in database 5. - DB metadata response 6. - Write METADATA_ACCESSED audit entry 7. - Return metadata object metadata 8. - Create API response from metadata 9. - Return HTTP metadata response Webhook entry points *1 - dms.response.objects |
Click here to show the metadata retrieval flow by ID (older version) >>
| 1. - HTTP get request to object URL 2. - Enrichment of request with authentication Token 3. - Query Metadata availability using Search Service 4. - Query objectId in ES 5. - Elastic Search version data response 6. - Return registry link if user is authorized for to access the object 7. - Retrieve metadata version using Registry Service 8. - Retrieve object version from data base 9. - Database object metadata response 10. - Return metadata object metadata 11.- Write METADATA_ACCESSED audit entry 12. - Create API response from metadata 13. - Return HTTP metadata response Webhook entry points *1 - dms.response.objects |
Search Queries
Already imported objects into the yuuvis® Momentum system can be queried using the provided core API's HTTP request with the search query as request body (POST /api/dms/objects/search).
>> CMIS-Based Query Language
Click here to show the search queries flow >>
| 1. - HTTP get request to object URL 2. - Enrichment of request with authentication Token 3. - Request query execution 4. - Translate and send ES query 5. - Recieve ES query results 6. - Return metadata object list 7. - Create API response from metadata 8. - Return HTTP metadata response Webhook entry points *1 - dms.request.search *2 - dms.response.objects |
Update Content
xxx
Click here to show the update content flow >>
| 1. - HTTP post request to content url of object 2. - Enrichment of the Request with authentication token 3. - Verify user has writing permissions on object using Search Service 4. - Query object in Elastic Search 5. - Return ElasticSearch query results 6. - Return User Authorization Verification results 7. - Infer analysis of new content item 8. - Commit new content to storage 9. - Content Storage Handling 9.1 - Using custom storage via Archive Service 9.2 - Using s3 interface of repository 10. - Update object metadata contentstream attribute 11. - Commit updated metadata to database and index 12. - Index the updated metadata in ES 13. - Write CONTENT_UPDATED audit entry 14. - Return updated metadata 15. - Create API response from metadata 16. - Return updated metadata Webhook entry points *1 - dms.response.objects |
xxx
Click here to show the update metadate flow >>
| 1. - HTTP post request to object id URL 2. - Enrichment of request with authentication token 3. - Query for objectId using Search Service to verify user Authorization 4. - Query Elasticsearch for object 5. - Elasticsearch object response (if user is properly authenticated) 6. - Authorization Test query response 7. - Infer metadata validation and update 8. - Commit updated metadata to index 9. - Index updated metadata in ES 10. - If Expiration Date has changed: update content storage via Archive Service 11. - Update metadata in Database 12. - Write METADATA_UPDATED audit entry 13. - Return updated metadata 14. - Create API response from metadata 15. - Return metadata HTTP response Webhook entry points *1 - dms.request.update.metadat *2 - dms.response.objects |
Deletion ...
xxx
Click here to show the deletion flow >>
| 1. - HTTP delete request to object id URL 2. - Enrichment of request with authentication token 3. - Query object using Search Service to verify user Authorization 4. - Query object in ElasticSearch 5. - ElasticSearch object reponse 6. - Authorization Verification Results 7. - Infer deletion of content 8. - Flag as deleted in ElasticSearch via Index 9. - Flag as deleted across Storage Providers 10. - Flag as deleted in Database 11. - Return deletion Status Code 12. - OBJECT_DELETED audit entry 13. - Return Deletion Results Webhook entry points *1 - dms.response.objects |
Summary
